Decoding RNA-RNA Interactions: The Role of Low-Complexity Repeats and a Deep Learning Framework for Sequence-Based Prediction
Abstract
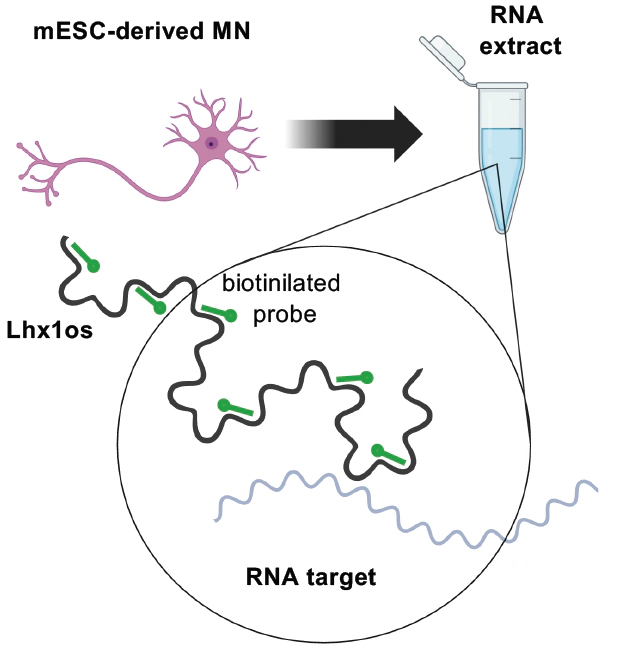
RNA-RNA interactions (RRIs) are fundamental to gene regulation and RNA processing, yet their molecular determinants remain unclear. In this work, we analyzed several large-scale RRI datasets and identified low-complexity repeats (LCRs), including simple tandem repeats, as key drivers of RRIs. Our findings reveal that LCRs enable thermodynamically stable interactions with multiple partners, positioning them as key hubs in RNA-RNA interaction networks. RNA-sequencing of the interactors of the Lhx1os lncRNA allowed to validate the importance of LCRs in shaping interactions potentially involved in neuronal development.Recognizing the pivotal role of sequence determinants, we developed RIME, a deep learning model that predicts RRIs by leveraging embeddings from a nucleic acid language model. RIME outperforms traditional thermodynamics-based tools, successfully captures the role of LCRs and prioritizes high-confidence interactions, including those established by lncRNAs.