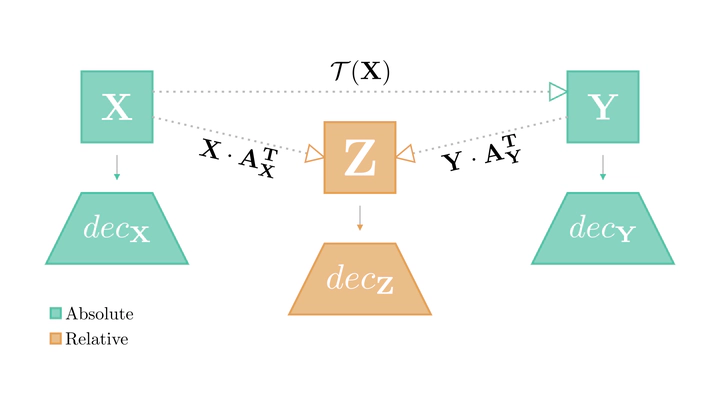
Abstract
Different neural models often exhibit similar latent spaces when exposed to semantically similar data; however, this inherent similarity may not always be immediately apparent. Leveraging this observation, our work shows how representations learned from these neural modules can be translated between different pre-trained networks via simpler transformations than previously thought. An advantage of this approach is the ability to estimate these transformations using standard, well-understood algebraic procedures that have closed-form solutions. Our method directly estimates a transformation between two given latent spaces, thereby enabling effective stitching of encoders and decoders without additional training. We extensively validate the adaptability of this translation procedure in different experimental settings: across various trainings, architectures (e.g., ResNet, CNN, ViT), and in multiple downstream tasks (classification, reconstruction). Notably, we show how it is possible to zero-shot stitch text encoders and vision decoders, or vice-versa, yielding surprisingly good classification performance in this multimodal setting.