Abstract
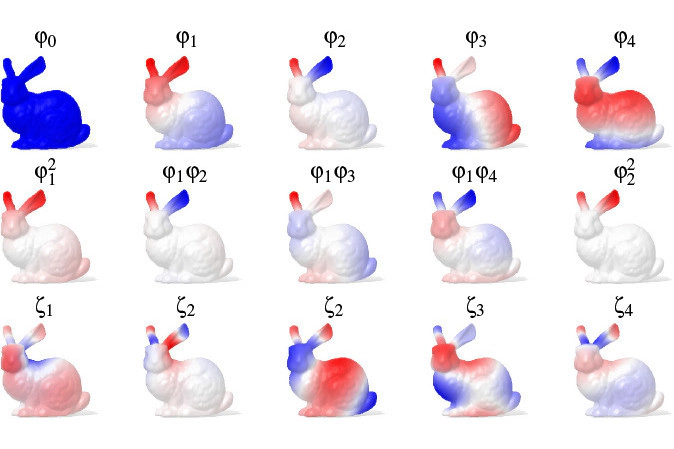
We propose a novel approach for the approximation and transfer of signals across 3D shapes. The proposed solution is based on taking pointwise polynomials of the Fourier-like Laplacian eigenbasis, which provides a compact and expressive representation for general signals defined on the surface. Key to our approach is the construction of a new orthonormal basis upon the set of these linearly dependent polynomials. We analyze the properties of this representation, and further provide a complete analysis of the involved parameters. Our technique results in accurate approximation and transfer of various families of signals between near-isometric and non-isometric shapes, even under poor initialization. Our experiments, showcased on a selection of downstream tasks such as filtering and detail transfer, show that our method is more robust to discretization artifacts, deformation and noise as compared to alternative approaches.