Abstract
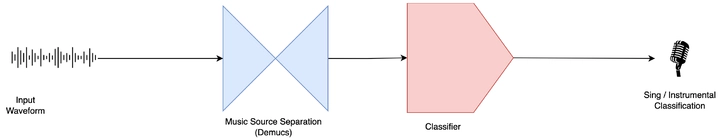
Singing voice detection (SVD) is an essential task in many music information retrieval (MIR) applications. Deep learning methods have shown promising results for SVD, but further performance improvements are desirable since it underlies many other tasks. This work proposes a novel SVD system combining a state-of-the-art music source separator (Demucs) with two downstream models: Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Network (LRCN) and a Transformer network. Our work highlights two main aspects: the impact of a music source separation model, such as Demucs, and its zero-shot capabilities for the SVD task; and the potential for deep learning to improve the system’s performance further. We evaluate our approach on three datasets (Jamendo Corpus, MedleyDB, and MIR-IK) and compare the performance of the two models to a baseline root mean square (RMS) algorithm and the current state-of-the-art for the Jamendo Corpus dataset.